Global and local variables – C/C++ Language
- Lucas
- September 01, 2011
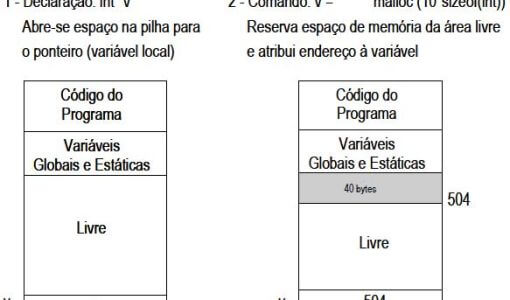
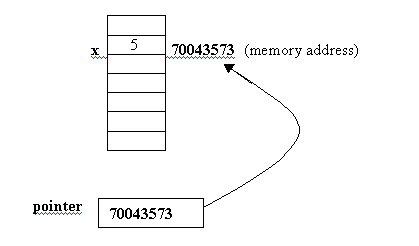
Global variables are variables declared outside a function, unlike local variables which are declared inside a function. #include int a = 1; // GLOBAL VARIABLE void main() { int b = 2; // LOCAL VARIABLE printf(“Value of variable ‘a’: %d”, a); printf(“\nValue of variable ‘b’: %d”, b); } When a variable is declared within a