Conditional If and Else in C

In C, a true expression is an expression that equals or returns any value other than 0 and a false expression equals or returns 0.
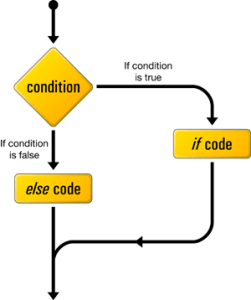
The general form of the If and Else sentence is:
if(condição) // Se a condição for verdadeira expressão; // Execute isso. else // Caso o contrário expressão; // Execute isso.
Example:
void main()
{
if(1 > 2)
printf("Verdadeiro");
else
printf("Falso");
}
In the example above, the “if” condition is executed, as 1 is not greater than 2, zero is returned and the expression is considered false, then the else is executed and the word “False” is displayed on the screen.
NOTE: A common mistake is to use the “=” sign when trying to buy whether two values are equal. In C it is worth remembering that the “=” sign is used for assignment and “==” for comparison, so when buying equality between two values you should use “==” instead of “=”.
Nested If and Else:
When more than one expression is placed within the If or Else condition, the expressions must be enclosed in braces as shown in the example:
void main()
{
if(1 && 2)
{
printf("Verdadeiro");
printf("Verdadeiro 2";
}
else
{
printf("Falso");
printf("Falso 2");
}
}