Comparison: CAT 6 vs. fiber optics. Which is better?

When it comes to choosing the best cabling solution for networks, two options are most often chosen: category 6 twisted pair cables (CAT 6) and fiber optics. Both transmission media have their particularities, benefits and limitations that make them more suitable for different types of applications and environments. In this article, we’ll explore the characteristics of each and indicate which option might be best for your specific needs.
General description
CAT 6 is an evolution of twisted pair cables used for data transmission in local area networks (LANs). This type of cable is widely used in residential and business environments due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation.
Optical fiber, on the other hand, uses pulses of light to transmit data instead of electrical signals, which allows for significantly higher transmission speeds and much greater distances. Its structure consists of a glass or plastic core that conducts light, surrounded by protective layers.

Speed and Bandwidth
CAT 6:
It offers a bandwidth of up to 250 MHz, supporting speeds of up to 1 Gbps (Gigabit Ethernet) over distances of up to 100 meters, and up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 55 meters. This is sufficient for most small to medium-sized home and corporate network applications.
Fiber optics:
It can reach bandwidths of over 100 GHz, depending on the type of fiber (singlemode or multimode). Supporting speeds of over 100 Gbps over distances of several kilometers. It is therefore ideal for applications requiring high transmission capacity and for infrastructures covering long distances, such as data centers and internet providers.
Transmission Distance
CAT 6:
It is most effective over short distances, usually up to 100 meters, but transmission quality begins to degrade beyond this limit, limiting the range in larger installations.
Fiber optics:
It can maintain high-quality transmission over much greater distances, reaching tens of kilometers (in the case of single-mode fiber). Ideal for interconnecting buildings, distant offices or even entire regions.
Immunity to Interference
CAT 6:
It is susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and noise from nearby electrical equipment, and can be affected in environments with high interference. However, shielding (in STP cables) can minimize this problem.
Fiber optics:
Immune to electromagnetic interference and noise, as it uses light signals instead of electrical signals. It is highly suitable for environments where signal integrity is critical, such as factories or places with a lot of electronic equipment.
Ease of Installation and Cost
CAT 6:
Cheaper and easier to install, both in terms of cabling and termination equipment (switches and routers), ideal for small and medium-sized businesses looking for a balance between cost and performance.
Fiber optics:
It costs more, both because of the material and the need for specialized equipment for installation and maintenance, also requiring greater technical training for installation and repair, which can increase operating costs.
Durability and maintenance
CAT 6:
Relatively durable, but more susceptible to physical damage and degradation over time, especially in harsh environments.
Fiber optics:
More durable and resistant to corrosion and harsh environmental conditions. However, it is more fragile in terms of bending and mishandling.
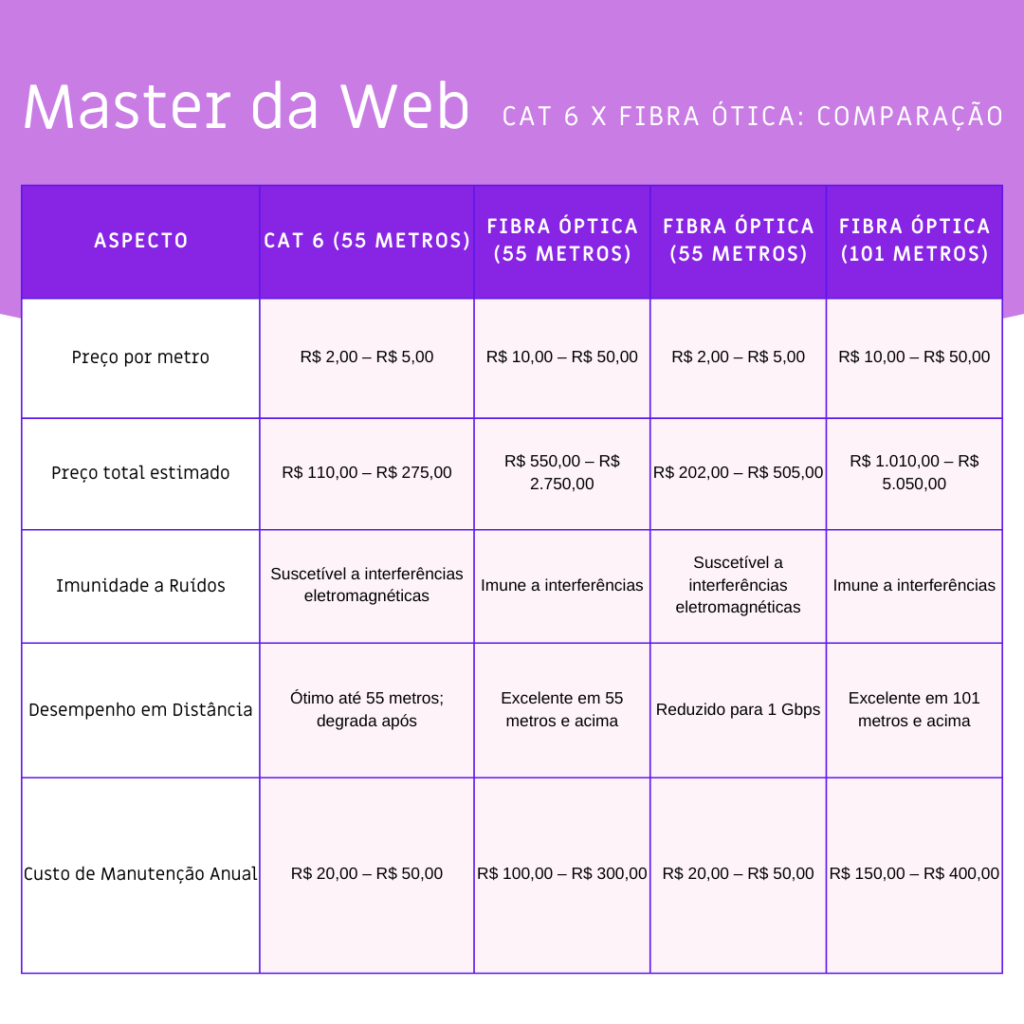
Table
Conclusion: Which is better?
The choice between CAT 6 and fiber optics depends largely on the application and the needs of the network.
For short-distance local networks, such as in offices and homes, and places where the cable can be handled quite easily, the strength, cost and ease of installation make CAT 6 the best choice.
On the other hand, for infrastructures that require very high speed, immunity to interference, long distances and secure cabling, fiber optics is the most suitable option, even if the initial investment is higher.
Each has its advantages, and the choice should be based on factors such as the size of the network, budget, performance requirements, the distance the network needs to cover and the necessary strength of the cabling. If the goal is to build a future-proof and expandable infrastructure, fiber optics certainly stands out as the most promising technology.