Raid is basically putting several HDDs and SSDs working together, with the intention of having + performance and security.

Raid 0: striping.
RAID 0 is the sum of the capacity and performance of both disks in a single logical disk format.
This way you get more performance and capacity, but it doesn’t offer any security.
If one of the disks fails, all the files will be lost.

Raid 1: mirroring.
Raid 1 adds nothing in terms of capacity and performance.
Normally used with two disks, it works as follows:
The files are mirrored between the disks, meaning that everything written to disk 1 is also written to disk 2.
This way you get the capacity and performance of just 1 disk, but if one of them stops working no files are lost. This way you can replace the defective disk so that mirroring can be redone.
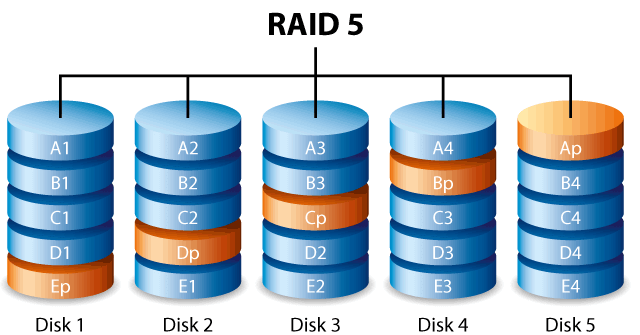
Raid 5: distribution with parity.
It is the most requested of the RAID configurations because of the security it provides. This is because data parity can quickly reconstruct information logically, even if a disk fails.
RAID 5 works with 3 or more identical hard drives of the same storage size, in some cases, depending on the controller, they need to be the same model. Parity is a calculation in hexadecimal format, meaning the replication of equal bits (0 and 1) spread across all the hard drives that make up the RAID ARRAY.
Data reconstruction happens automatically via the controller when a disk fails and goes offline. Once this has happened, the controller automatically allocates the parity information to the operating system and, in some cases, this slows things down a bit, requiring the bad disk to be removed and replaced.
This will enable a fast and safe environment again.
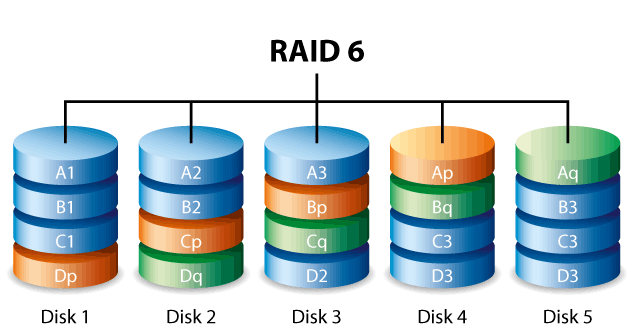
RAID 6: distribution with double parity.
Raid 6 is an evolution of RAID 5. By recording data with two layers of parity bits, this arrangement allows up to two disks to fail in the same set without data loss.
The security obtained by writing double parity sacrifices performance and delivers less capacity when compared to single parity arrangements.
This means that in a storage where four hard disks will be installed in RAID 6, only the space equivalent to two will be available for use.
This type of configuration offers good fault tolerance and is used in environments where the security of stored data is a priority.
The loss of performance caused by double-writing the parity bits in the recorded data can be compensated for by assembling arrays larger than four disks, because the more disks in the array, the faster the data will be written.
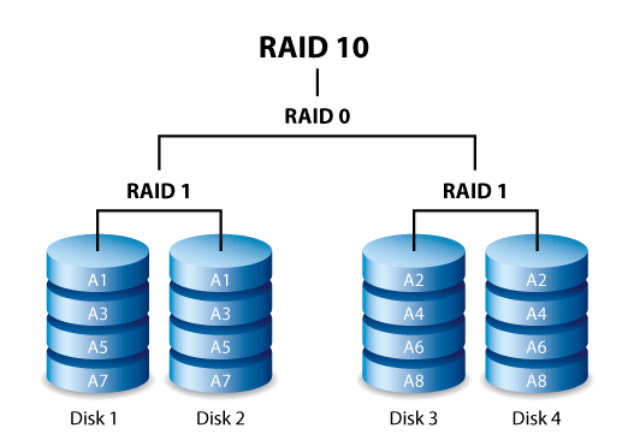
RAID 10: combining mirroring and striping.
Raid 10 combines the advantages of raid 0 and raid 1, adding performance, capacity and security.
Requiring 4 disks or more, raid 10 works as follows:
The files are distributed in two arrays, adding up the capacity and performance of both, so if 2 disks stop, no files are lost. You can then swap the damaged disks to mirror them again.
Raid 10 is suitable for those looking for + capacity + performance and who don’t want to compromise on security
ATTENTION:
Working with RAID gives you more redundancy and security.
This doesn’t mean that you don’t have to back up, because if all the hard drives stop working at the same time, no matter which raid you’re using, you’ll lose all your files.
Always make a backup, don’t leave your important files at risk.